Imaging
The Imaging Unit provides diagnostic and interventional procedures to our patients. The unit is staffed with experienced radiologists, radiographers, staff nurses and other support staff who specialise in imaging services. Our top-tier facilities ensure accurate and prompt imaging services. The Diagnostic Imaging services include:
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine is a branch of medical imaging, which uses a small amount of radioactive substance injected into the body, inhaled or swallowed, to diagnose and treat a variety of diseases including cancers, gastrointestinal, heart disease, endocrine and neurological disorder. It is often able to identify abnormalities very early in the progression of a disease, long before many medical problems are apparent with other diagnostic tests.
After diagnosis, and when treatment starts, these scans continue to play an important role in monitoring its effects and progress of treatment regime, to determine if modification of therapy is required.
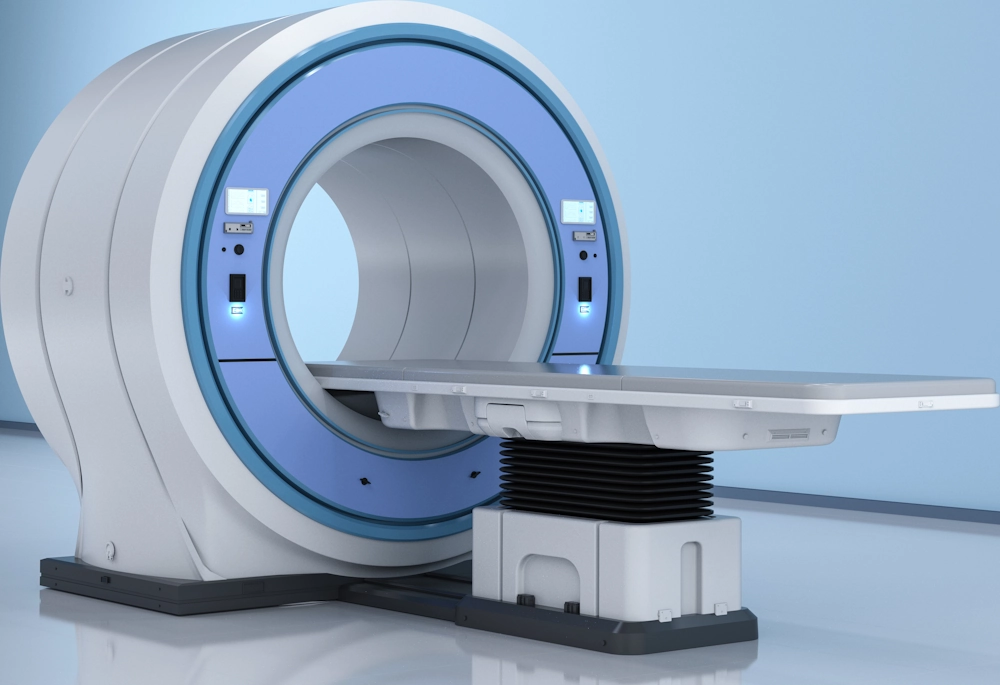
Established in 2018, the Advance Nuclear Diagnostic and Therapeutic Centre @ PHKL is equipped with cutting-edge advanced technology in Nuclear Medicine (PET-CT & SPECT-CT) to deliver accurate structural and functional imaging of the body for diagnosis and management of cancer and other diseases. This allows for tailored individualised treatment plans for our patients, which translate to better prognosis and outcomes for our patients.
Biograph mCT S 64 PET-CT
READ MORE
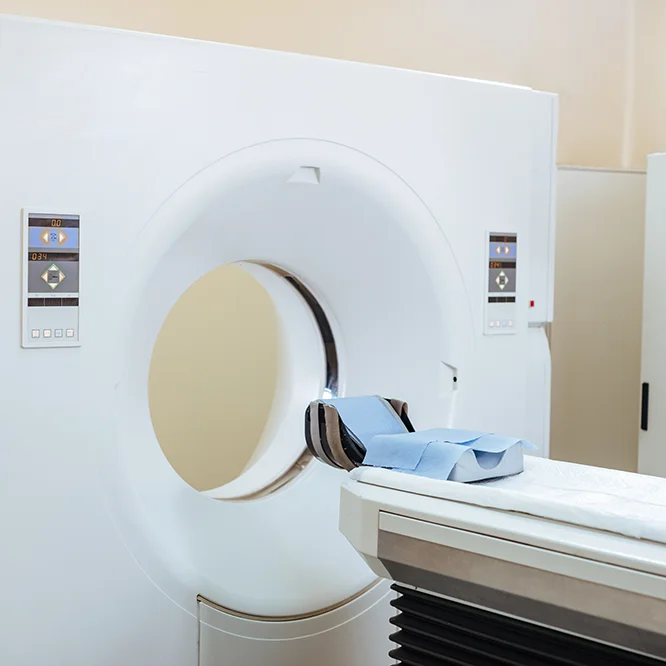
Symbia Intevo
T16 SPECT-CT
READ MORE

Why Choose Us?

450
Licensed
Beds

30+
Treatment
Modalities

26
Chemo
Bay

38
Medical
Specialities

200+
Specialist
Doctors
30,000+
Patient
Served



.webp?sfvrsn=3e05baf9_1)